간암에서 JX-594 항암 바이러스를 이용한 임상시험
이 논문에 등장하는 환자 30명 중 13명이 한국 환자이며… 현재 7개국 120명의 간암, 대장암,
신장암 등 암 환자를 대상으로도 국제 임상시험을 하고 있는데… 한국이 임상시험을 주도하고
있음.
============
Randomized dose-finding clinical trial of oncolytic immunotherapeutic vaccinia JX-594 in liver cancer
- Journal name:
- Nature Medicine
- Year published:
- (2013)
- DOI:
- doi:10.1038/nm.3089
- Received
- Accepted
- Published online
Abstract Figure 1: Radiographic antitumor activity after JX-594 therapy determined by dynamic MRI with a central radiographic reader blinded to treatment group. 
(a) Greatest decrease in the sum of the longest diameter (LD) of target tumors from baseline (mRECIST criteria) in livers of individual patients after JX-594 treatment. n = 22 patients who had measurable and evaluable tumors at baseline and at least one follow-up time point. A tumor with an increase >100% is indicated with a + above the bar. (b) Greatest decrease in tumor contrast enhancement or longest diameter from baseline (Choi criteria) in target tumors in livers of individual patients after JX-594 treatment. n = 24 patients who had measurable and evaluable tumors at baseline and at least one follow-up time point. A tumor with an increase >100% is indicated with a + above the bar. (c) Greatest decrease in the sum of the longest tumor diameter from baseline (RECIST criteria) in noninjected liver tumors of individual patients after JX-594 treatment. n = 8 evaluable. (d) Greatest decrease in tumor contrast enhancement or longest diameter from baseline (Choi criteria) in noninjected liver tumors of individual patients after JX-594 treatment. n = 8 evaluable. (e) Example of the effects of JX-594 on contrast enhancement and perfusion in an injected tumor (JX7-1401; high dose). (f) Example of the effects of JX-594 on the longest diameter of an injected tumor (complete mRECIST response) (JX7-1715; low dose). (g) Example of the effects of JX-594 on contrast enhancement and perfusion in a noninjected (distant) tumor (JX7-1403; high dose). The red circles (e–g) indicate the same (responding) tumors over time.
Figure 2: Laboratory evidence for JX-594 replication, transgene expression and GM-CSF protein function. 
(a) The mean (± s.e.m.) peak concentration of JX-594 (genomes measured by quantitative PCR (qPCR)) in blood after each treatment cycle (using blood obtained 15 min after the completion of treatment) by dose group (t test). IT, intratumoral. (b) The percentage of patients with evidence of β-gal transgene expression (+95% confidence interval (CI)) after JX-594 treatment (generation of antibodies (Ab) to the β-gal transgene product within 29 d of treatment is indicative of JX-594 replication, as β-gal protein expression is associated with virus replication) (Fisher’s exact test). (c) The percentage of patients with evidence of hGM-CSF transgene expression (+95% CI) on day 5 after JX-594 treatment (Fisher’s exact test). (d) Maximum induction of neutrophil concentration in blood after treatment cycle 1 by dose group (using blood obtained on days 5 and 15 after treatment). Black bars, low-dose JX-594; white bars, high-dose JX-594.
Figure 3: Laboratory, radiographic and biopsy evidence for JX-594–associated induction of anticancer immunity. 
(a) Antibody-mediated complement-dependent cytotoxicity induction after JX-594 therapy in HCC (n = 4), normal (n = 2; HUVEC and MRC-5) and non-HCC (RCC, n = 3; melanoma, n = 4) cell lines. Each graph shows the mean percentage cell viability (+s.d.) after incubation with each individual patient’s serum (diluted to 5%) collected on day 43 after the initiation of treatment compared to baseline. JX7-1704 and JX7-1702, two high-dose patients. (b) Antibody-mediated CDC induction against HCC cell lines in individual patients over time after JX-594 therapy (serum diluted to 5%; mean ± s.d.). The data shown are from serum of patients that induced ≤50% cell viability (>50% cell killing) on at least one follow-up time point. (c) Radiographic evidence of progressive necrosis and peripheral enhancement over time in noninjected tumors (JX7-0307; low dose). (d) H&E staining of a biopsy sample from a tumor collected from patient JX7-0301 (low dose) 1.5 years after the initiation of JX-594 treatment. Scale bars, 100 μm (low magnification); 50 μm (high-magnification inset). (e) Radiographic evidence of progressive necrosis and peripheral enhancement over time in a noninjected tumor (JX7-0301; low dose). Red circles (c,e) indicate the same (responding) tumors over time. (f) ELISPOT analysis detecting T cells producing interferon-γ in response to stimulation with β-gal peptides at baseline and after JX-594 treatment; data are expressed as the mean number of spot-forming cells (SFC) per 105 cells (+s.d.) (JX7-0310, low dose; JX7-0311, high dose). (−), negative control peptide. The P values in a and f were calculated by t test.
Figure 4: Kaplan-Meier analysis of overall survival. 
(a) Overall survival in the entire evaluable study population (dashed line) and by dose group (n = 29 total). (b) Overall survival in subjects with multiple tumors at baseline (ten high-dose and nine low-dose subjects). (c) Overall survival in the entire evaluable study population by the presence or absence of baseline neutralizing antibody status. (d) Overall survival in high-dose subjects having previously failed systemic therapy (n = 6).
Oncolytic viruses and active immunotherapeutics have complementary mechanisms of action (MOA) that are both self amplifying in tumors, yet the impact of dose on subject outcome is unclear. JX-594 (Pexa-Vec) is an oncolytic and immunotherapeutic vaccinia virus. To determine the optimal JX-594 dose in subjects with advanced hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC), we conducted a randomized phase 2 dose-finding trial (n = 30). Radiologists infused low- or high-dose JX-594 into liver tumors (days 1, 15 and 29); infusions resulted in acute detectable intravascular JX-594 genomes. Objective intrahepatic Modified Response Evaluation Criteria in Solid Tumors (mRECIST) (15%) and Choi (62%) response rates and intrahepatic disease control (50%) were equivalent in injected and distant noninjected tumors at both doses. JX-594 replication and granulocyte-macrophage colony-stimulating factor (GM-CSF) expression preceded the induction of anticancer immunity. In contrast to tumor response rate and immune endpoints, subject survival duration was significantly related to dose (median survival of 14.1 months compared to 6.7 months on the high and low dose, respectively; hazard ratio 0.39; P = 0.020). JX-594 demonstrated oncolytic and immunotherapy MOA, tumor responses and dose-related survival in individuals with HCC.
At a glance
=================
말기 간암에 탁월한 효능있다”는 바이러스는…
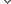
조선일보 입력 : 2013.02.13 03:17 | 수정 : 2013.02.13 09:07
http://news.chosun.com/site/data/html_dir/2013/02/13/2013021300044.html?news_Head1
말기 간암에 탁월한 효과… 국내 연구진 주도로 확인
정상 세포는 공격하지 않고 암세포에 기생해 죽이는 원리 “이르면 5년 후 상용화 가능”
일부 환자, 2년 넘게 생존중 다른 암도 효과있는지 연구
천연두 박멸의 1등 공신인 우두 바이러스가 말기 간암에도 효험이 탁월하다는 사실이 한국 연구진이 주도한 국제 공동 연구를 통해 확인됐다. 부산대 황태호 교수(항암바이오연구소)를 비롯한 한국 연구진과 미국·캐나다 연구진 등으로 이뤄진 공동 연구팀은 유전자를 변형한 우두 바이러스가 말기 간암 환자의 생존 기간을 기존 항암제보다 최소 2~3배 이상 늘린다는 임상시험 결과를 12일 발표했다. 시험 결과는 세계적인 과학 저널 네이처의 의학 분야 자매지인 ‘네이처 메디신(Nature Medicine)’에 실렸다.
연구진은 우두 바이러스가 암세포만 공격하도록 만들었다. 암세포와 바이러스에서 공통적으로 발견되는 ‘TK 유전자’를 조작한 것이 핵심 비결이었다. 이 유전자는 암이나 바이러스의 증식을 촉진하는 TK 효소를 분비한다. 연구진은 우두 바이러스의 TK 유전자가 작동하지 못하도록 유전자를 변형했다. 증식에 필요한 효소를 분비할 수 없게 된 바이러스는 암 환자의 몸에 들어가면 암세포에 기생하면서 TK 효소를 빼앗아 자신이 증식하는 데 사용한다. 암세포는 그 여파로 증식하지 못하고 결국 죽게 되는 것이다. 바이러스는 TK 유전자가 없는 정상 세포는 공격하지 않는다.
연구진은 이렇게 만든 항암 바이러스를 말기 간암 환자 30명에게 한 달간 투여했다. 그 결과 저용량 바이러스를 맞은 15명은 평균 6.7개월, 고용량 바이러스를 맞은 나머지 15명은 평균 14.1개월을 더 생존했다. 특히 최고 용량을 맞은 환자는 2년 넘게 생존하고 있다고 연구진은 밝혔다. 기존 간암 치료제는 말기 환자의 생존 기간이 평균 3개월이었다.
JX-594라고 이름 붙여진 이 항암 바이러스는 미국 제네렉스(Jennerex)사가 최초 개발을 시작했다. 이 과정에서 부산대 황태호 교수 연구진과 연세대 의대, 성균관대 의대, 녹십자 등이 참여했다. 공동 연구였지만 임상시험은 한국이 주도했다. 이번 논문에 등장하는 환자 30명 중 13명도 한국 환자였다.
제네렉스 데이비드 컨 박사와 함께 10여년째 연구를 주도하고 있는 황태호 교수는 “JX-594는 현재 7개국 120명의 간암 환자뿐만 아니라 대장암과 신장암 등 다른 암 환자를 대상으로도 국제 임상시험을 하고 있다”며 “이르면 4~5년 정도면 상용화가 가능할 것으로 본다”고 말했다.
☞우두(牛痘) 바이러스
소 마마로 불리는 질병을 일으키는 바이러스. 1796년 영국의 에드워드 제너가 우두에 걸린 소의 고름을 이용해 천연두 예방접종인 종두를 개발했다.